Contatto
Siamo a vostra disposizione da lunedì a venerdì dalle ore 8:00 alle ore 17:00. In questo link troverete le persone di contatto per la vostra regione.
Sede di Wolfurt
+43 5574 6706-0
Carrello acquisti {{ (warenkorbCtrl.warenkorb.bestellNummer ? (' [' + warenkorbCtrl.warenkorb.bestellNummer + '] ') : '' )}} | {{warenkorbCtrl.warenkorb.items.length}} Articoli Cambia carrello acquisti
Nota
| Foto | Articoli | Pz. | Prezzo singolo | Prezzo unitario | Prezzo unitario incluso lo sconto | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
{{warenkorbItem.produktgruppe.produktname}}{{warenkorbItem.bezeichnung | artikelBezFilter:warenkorbItem.attributwertEingaben:[{attrPrefix: 'L_', searchPattern: '/...', replacePrefix: '/', replaceSuffix: ''}] }} {{warenkorbItem.bezeichnung | artikelBezFilter:warenkorbItem.attributwertEingaben}}
{{attributwertEingabe.attributBezeichnung}}
|
|
||||
{{hannexItem.Benennung}}{{hannexItem.Bezeichnung}} |
|
-
Clienti
- Costruzione stampi
- Stampi per tranciatura
- Costruzione macchine e dispositivi
- Progettisti
- Stampaggio ad iniezione
-
Prodotti
- Nuovi prodotti
- Portastampi
-
Basi portastampo
- La base portastampo standard SV
- Basi portastampo di precisione SP
- Base portastampo a due colonne con guida posteriore SH
- Base portastampo diagonale a due colonne SD
- Base portastampo centrale a due colonne SZ
- Tecnica modulare SM
- BASI PORTASTAMPO TRANCIA-PIEGATRICI SB
- Sistema di staffaggio H 3000
- Piastre P
- Barre N
- Piastre e barre
- Lavorazioni speciali
- Accessori E
- Tecnica del canale caldo
- Termoregolazione canale caldo
- Prodotti per l‘officina
- Azienda
- Carriera
- Servizio clienti

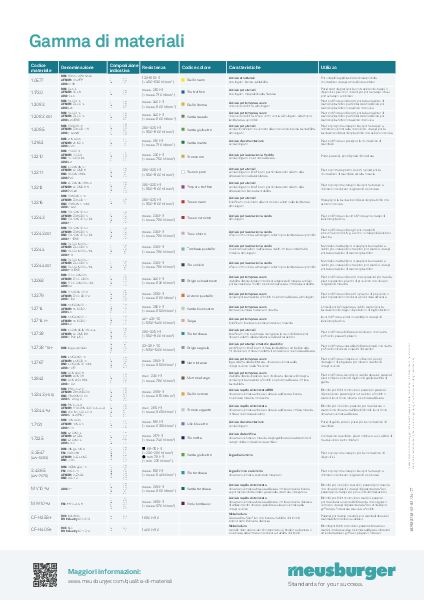
La nostra vasta gamma permette di trovare il materiale idoneo per quasi tutte le applicazioni.
1.2767 Steel for through hardening
Designation
| DIN: | 45 NiCrMo 16 |
| AFNOR: | 45 NCD 16 |
| UNI: | 40 NiCrMoV 16 KU |
| AISI: | ≈ 6F7 |
Chemical composition:
| C | 0.45 |
| Si | 0.25 |
| Mn | 0.40 |
| Cr | 1.35 |
| Mo | 0.25 |
| Ni | 4.00 |
Strength:
max. 280 HB
(≈ max. 950 N/mm²)
Thermal conductivity at 100 °C:
30 W/m K
Character:
Nickel alloyed steel for through hardening, with moderate machinability; very high resistance against bending and high compressive strength; very high toughness and good through hardenability, also with bigger sections.
Application:
high-performance cavity plates and inserts for the processing of plastics with high surface requirements (mirror finish); stamping, forming and bending dies for particularly high pressure and bending stresses
Treatment by
Polishing:
best metallurgical properties for mirror finish
is possible:
Etching
highly suitable:
EDM
not usual:
Nitriding
Hard chroming:
particularly increases the steel's wear resistance and corrosion resistance
Heat treatment:
Soft annealing:
610 to 650 °C for about 2 to 5 hours slow controlled cooling of 10 to 20 °C per hour to about 600 °C further cooling in air, max. 260 HB
Hardening:
840 to 870 °C
Quenching in oil/hot bath/air
Obtainable hardness: 53-58 HRC
Tempering:
Slow heating to tempering temperature immediately after hardening. Minimum time in furnace: 1 hour per 20 mm part thickness. Tempering twice is recommended.
Annealing graph:

Technical tip:
- To avoid unwanted warping during plastic injection, the tempering temperature after hardening must exceed the operating temperature by 50 °C.
Example:
operating temperature is 200 °C
tempering at 250 °C = 52 HRC
Vai alla panoramica per la costruzione stampi Vai alla panoramica per la costruzione stampi per tranciatura
Available in the web shop as:
Data sheet 1.2767
Azienda
Meusburger Georg GmbH & Co KG
Kesselstr. 42
6960 Wolfurt | Austria
+43 5574 6706
office@meusburger.com
@ 2024 Meusburger
 © 2024 by Meusburger Georg GmbH & Co KG | All rights reserved
© 2024 by Meusburger Georg GmbH & Co KG | All rights reserved



 P-Standard plates
P-Standard plates

 NP-Precision bars
NP-Precision bars NR-Round bars
NR-Round bars NE-Blocks for eroding
NE-Blocks for eroding





 Česká republika [CS]
Česká republika [CS]
 Danmark [DA]
Danmark [DA]
 Deutschland [DE]
Deutschland [DE]
 España [ES]
España [ES]
 France [FR]
France [FR]
 India [EN]
India [EN]
 Italia [IT]
Italia [IT]
 Magyarország [HU]
Magyarország [HU]
 México [ES]
México [ES]
 Nederland [NL]
Nederland [NL]
 Österreich [DE]
Österreich [DE]
 Polska [PL]
Polska [PL]
 Portugal [PT]
Portugal [PT]
 România [RO]
România [RO]
 Schweiz [DE]
Schweiz [DE]
 Slovenija [SL]
Slovenija [SL]
 Srbija [SR]
Srbija [SR]
 Suomi [FI]
Suomi [FI]
 Sverige [SV]
Sverige [SV]
 Türkiye [TR]
Türkiye [TR]
 United Kingdom [EN]
United Kingdom [EN]
 USA [EN]
USA [EN]
 Ελλάδα [EL]
Ελλάδα [EL]
 България [BG]
България [BG]
 Росси́я [RU]
Росси́я [RU]
 华 [ZH]
华 [ZH]